Delve into the Captivating Realm of Dolphin Anatomy
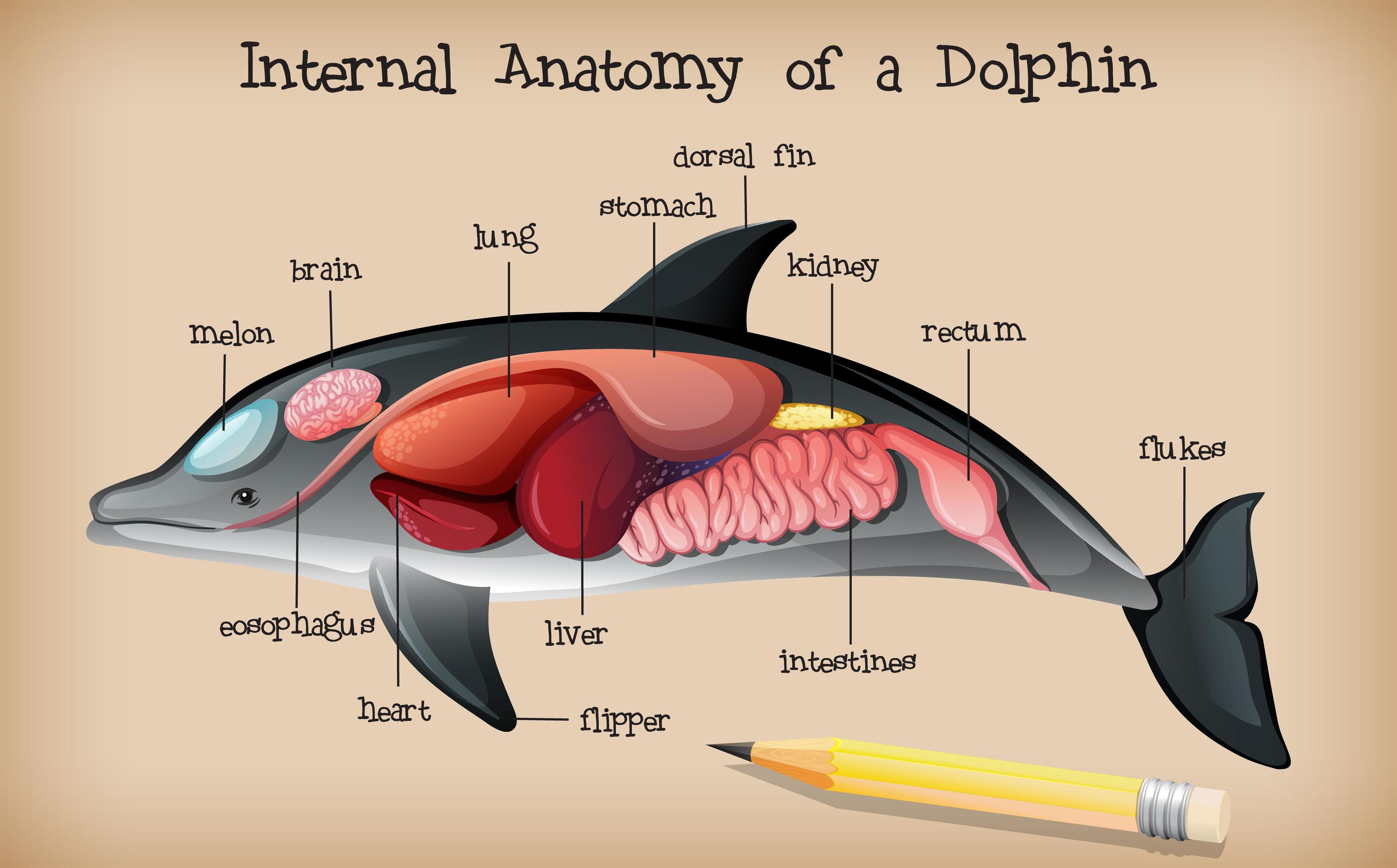
The anatomy of dolphins, marine mammals renowned for their intelligence and playful nature, presents an extraordinary study in adaptation and evolution. These aquatic wonders possess a unique set of physical attributes that enable them to thrive in their oceanic habitat.
Dolphin Anatomy: A Symphony of Adaptations
Dolphins exhibit a streamlined body shape, optimized for reducing drag and facilitating rapid swimming. Their skin, smooth and supple, is covered in a thin layer of blubber, providing insulation and buoyancy. The absence of hind limbs and the presence of a powerful fluke (tail fin) propel them through the water with remarkable efficiency.
Their sensory organs are highly specialized. Dolphins possess exceptional echolocation abilities, enabling them to navigate and locate prey using sound waves. Their large eyes, positioned on the sides of their head, provide a wide field of vision both above and below the water's surface.
Internally, dolphins have a complex respiratory system adapted to underwater. Their lungs are small and compact, allowing for rapid gas exchange during brief surface intervals. The circulatory system is efficient, distributing oxygen and nutrients throughout the body with remarkable speed.
- New Keith Urban Hits Albums Country Music Star
- Christina Aguileras Stunning Weight Loss Transformation
Evolutionary Significance and Ecological Importance
The anatomy of dolphins reflects millions of years of evolutionary adaptation to their marine environment. Their streamlined bodies, specialized sensory organs, and efficient respiratory system have enabled them to become apex predators, occupying a vital role in the oceanic ecosystem.Conclusion
The anatomy of dolphins is a testament to the remarkable diversity and ingenuity of nature. These fascinating creatures, with their unique physical attributes and intelligent behavior, continue to captivate and inspire us. Their study provides valuable insights into the wonders of marine life and the importance of preserving our oceans and its inhabitants.Anatomy of a Dolphin
The anatomy of a dolphin is a fascinating study in adaptation and evolution. These marine mammals have evolved a unique set of physical characteristics that allow them to thrive in their oceanic environment.
- Streamlined body
- Smooth skin
- Powerful fluke
- Echolocation
- Large eyes
- Small lungs
- Efficient circulatory system
These key aspects of dolphin anatomy work together to create a creature that is perfectly adapted to its environment. The streamlined body and smooth skin reduce drag and allow dolphins to swim quickly and efficiently. The powerful fluke provides propulsion, while the echolocation system helps dolphins navigate and find prey. The large eyes give dolphins a wide field of vision, and the small lungs and efficient circulatory system allow them to stay underwater for long periods of time.
Dolphins are also known for their intelligence and social behavior. They live in pods of up to 100 individuals and communicate with each other using a complex system of clicks and whistles. Dolphins are also known to play and engage in cooperative hunting behaviors.
The anatomy of a dolphin is a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of life on Earth. These amazing creatures have evolved over millions of years to become one of the most successful predators in the ocean.
1. Streamlined body
The streamlined body of a dolphin is a key adaptation that allows these marine mammals to swim quickly and efficiently through the water. The dolphin's body is shaped like a torpedo, with a smooth, rounded surface that minimizes drag. The dolphin's skin is also very smooth, with no scales or other protrusions that could create drag. The dolphin's body is also very flexible, which allows it to swim through the water with a minimum of resistance.
The streamlined body of a dolphin is essential for its survival. Dolphins are predators that rely on speed and agility to catch their prey. The streamlined body allows dolphins to swim quickly and quietly, so that they can surprise their prey. The streamlined body also helps dolphins to conserve energy, which is important for long-distance swimming.
The streamlined body of a dolphin is a marvel of engineering. It is a testament to the power of evolution and adaptation. The dolphin's streamlined body is a key reason why these marine mammals are such successful predators and why they are able to thrive in the ocean environment.
2. Smooth skin
The smooth skin of dolphins is another key adaptation that allows them to swim quickly and efficiently through the water. The dolphin's skin is covered in a thin layer of blubber, which helps to keep the dolphin warm and buoyant. The skin is also very elastic, which allows the dolphin to stretch and contract its body as it swims.
- Reduced drag
The smooth skin of dolphins helps to reduce drag as they swim through the water. This is because the smooth surface of the skin does not create any turbulence or eddies, which can slow down the dolphin. The smooth skin also helps to keep the dolphin's body streamlined, which further reduces drag.
- Increased speed
The reduced drag that results from the dolphin's smooth skin allows the dolphin to swim faster. Dolphins are able to reach speeds of up to 35 miles per hour (56 kilometers per hour) in short bursts. This speed is essential for dolphins to catch their prey and escape from predators.
- Improved agility
The smooth skin of dolphins also helps to improve their agility. Dolphins are able to change direction quickly and easily, which is important for catching prey and avoiding predators. The smooth skin also allows dolphins to swim through tight spaces, such as coral reefs.
- Protection from injury
The smooth skin of dolphins also helps to protect them from injury. The thick layer of blubber helps to cushion the dolphin's body from impacts. The smooth skin also helps to prevent the dolphin from getting cuts and abrasions.
The smooth skin of dolphins is a key adaptation that allows these marine mammals to survive and thrive in the ocean environment. The smooth skin helps to reduce drag, increase speed, improve agility, and protect the dolphin from injury.
3. Powerful fluke
The powerful fluke, or tail fin, of a dolphin is a key anatomical feature that enables these marine mammals to swim quickly and efficiently through the water. The fluke is a broad, flattened structure that is located at the posterior end of the dolphin's body. It is composed of two lobes that are connected by a thick band of muscle. When the dolphin contracts these muscles, it causes the fluke to move up and down, propelling the dolphin through the water.
The fluke is a very powerful structure. It is capable of generating a great deal of thrust, which allows dolphins to swim at high speeds. Dolphins have been clocked at speeds of up to 35 miles per hour (56 kilometers per hour) in short bursts. The fluke is also used for steering and maneuvering. Dolphins can use their flukes to change direction quickly and easily, which is important for catching prey and avoiding predators.
The powerful fluke is an essential anatomical feature for dolphins. It allows them to swim quickly, efficiently, and maneuverably. These abilities are essential for dolphins to survive and thrive in the ocean environment.
Echolocation
Echolocation is a fascinating ability possessed by dolphins that allows them to navigate and hunt in murky or dark waters. It involves emitting high-pitched sounds and interpreting the echoes that bounce back from objects in the environment. This process provides dolphins with a detailed "sonic map" of their surroundings.
- Biosonar
Dolphins produce a series of clicks and whistles through a specialized organ in their head called the melon. These sounds are emitted in a narrow beam and travel through the water at high speeds.
- Echo Reception
The dolphin's sensitive lower jawbone receives the returning echoes. Specialized fatty tissues in the jaw conduct the sound waves to the inner ear, where they are processed by the auditory system.
- Image Creation
The dolphin's brain rapidly assembles the incoming echoes into a mental image of its surroundings. This image provides information about the location, size, and shape of objects, allowing the dolphin to navigate and find prey.
- Precision and Accuracy
Echolocation in dolphins is incredibly precise and accurate. They can distinguish between objects just a few centimeters apart and detect small variations in texture and density.
Echolocation is a remarkable adaptation that has evolved in dolphins over millions of years. It is a key component of their anatomy, enabling them to survive and thrive in their oceanic environment. By using echolocation, dolphins can navigate complex underwater landscapes, find prey in low-visibility conditions, and communicate with each other.
4. Large eyes
Dolphins possess large eyes that are strategically positioned on the sides of their head, providing them with a wide field of vision. These large eyes are an essential component of their anatomy, contributing significantly to their survival and success in their marine environment.
One of the primary functions of the dolphin's large eyes is to facilitate clear and efficient vision in diverse underwater conditions. The eyes are adapted to low-light environments, enabling dolphins to navigate murky waters and deep depths where sunlight penetration is limited. Their large pupils allow them to capture more light, enhancing their vision in these challenging conditions.
Furthermore, the position of the dolphin's eyes provides them with a panoramic view, allowing them to simultaneously observe their surroundings above and below the water's surface. This wide field of vision is crucial for detecting predators, locating prey, and maintaining group cohesion during pod activities.
The large eyes of dolphins also contribute to their exceptional depth perception, which is essential for accurate navigation and maneuverability in their three-dimensional underwater environment. Dolphins rely on visual cues to navigate complex underwater landscapes, avoid obstacles, and hunt for food. Their large eyes provide them with the necessary visual acuity to perform these tasks effectively.
In conclusion, the large eyes of dolphins are a vital component of their anatomy, enabling them to excel in their marine environment. Their wide field of vision, low-light adaptation, and depth perception enhance their ability to navigate, hunt, and interact with their surroundings. Understanding the significance of large eyes in dolphin anatomy provides valuable insights into the adaptations and survival mechanisms of these remarkable marine mammals.
5. Small lungs
Dolphins, despite being marine mammals, possess relatively small lungs compared to terrestrial mammals of similar size. This unique anatomical feature is closely linked to their exceptional diving capabilities and efficient oxygen utilization.
The small lung capacity of dolphins is an adaptation that allows them to make deep and prolonged dives without experiencing decompression sickness or oxygen toxicity. When a dolphin dives, its heart rate slows down, and blood is diverted away from the extremities and non-essential organs to prioritize oxygen delivery to the brain and vital organs. This adaptation enables dolphins to conserve oxygen and remain submerged for extended periods, often exceeding 10 minutes.
Furthermore, the small lungs of dolphins have a high density of capillaries, which facilitates efficient gas exchange. The rapid diffusion of oxygen across these capillaries allows dolphins to extract maximum oxygen from each breath, further enhancing their diving abilities. The efficient oxygen utilization and small lung capacity are crucial for dolphins to successfully hunt for prey, evade predators, and navigate their underwater environment.
Understanding the connection between small lungs and dolphin anatomy provides insights into the remarkable adaptations that enable these marine mammals to thrive in their aquatic habitat. By studying the physiological mechanisms and evolutionary pressures that have shaped dolphin anatomy, scientists gain valuable knowledge about the diversity and resilience of life in the oceans.
6. Efficient Circulatory System
The efficient circulatory system of dolphins is a vital component of their anatomy, playing a crucial role in supporting their unique adaptations and survival in the marine environment.
- Cardiovascular Capacity
Dolphins possess a robust cardiovascular system with a large heart and thick blood vessel walls, enabling them to pump blood efficiently throughout their bodies. This adaptation allows dolphins to maintain high blood pressure, providing the necessary oxygen and nutrients to their tissues and organs, even during deep dives.
- Oxygen Conservation
The circulatory system of dolphins is designed to conserve oxygen during dives. When a dolphin submerges, its heart rate slows down significantly, reducing metabolic activity and oxygen consumption. This adaptation allows dolphins to remain underwater for extended periods, often exceeding 10 minutes.
- Heat Retention
The circulatory system also plays a role in thermoregulation. Dolphins have a thick layer of blubber that insulates their bodies and helps retain heat. The circulatory system efficiently distributes blood throughout the body, ensuring that vital organs maintain optimal temperature, even in cold waters.
- Blood Volume
Dolphins have a relatively large blood volume compared to other mammals of similar size. This increased blood volume provides a greater oxygen reservoir, allowing dolphins to meet the high metabolic demands of swimming and diving.
The efficient circulatory system of dolphins is a testament to their remarkable adaptations for life in the ocean. By understanding the components and functions of this system, scientists gain valuable insights into the physiological mechanisms that enable dolphins to thrive in their unique environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Dolphin Anatomy
This section provides answers to common questions and misconceptions surrounding dolphin anatomy, offering a comprehensive understanding of these remarkable marine mammals.
Question 1: Why do dolphins have a streamlined body shape?
Answer: The streamlined body shape of dolphins is an adaptation for efficient swimming. It reduces drag in the water, allowing dolphins to move quickly and conserve energy, which is crucial for hunting and avoiding predators.
Question 2: What is the function of the dolphin's fluke?
Answer: The fluke, or tail fin, is a powerful structure that propels dolphins through the water. By contracting the muscles in the fluke, dolphins can generate significant thrust, enabling them to swim at high speeds, change direction rapidly, and maintain stability while diving.
Question 3: How do dolphins use echolocation?
Answer: Echolocation is a remarkable ability of dolphins to navigate and locate prey in murky or dark waters. They emit high-pitched sounds and interpret the returning echoes to create a detailed mental image of their surroundings. This allows them to detect objects, determine their size and shape, and even distinguish between different types of prey.
Question 4: Why do dolphins have large eyes?
Answer: The large eyes of dolphins are adapted for excellent vision in both air and water. They have a wide field of view, enabling them to scan their surroundings above and below the water's surface, which is essential for detecting predators, finding food, and maintaining group cohesion.
Question 5: How do dolphins conserve oxygen during dives?
Answer: Dolphins have several adaptations that allow them to conserve oxygen during deep dives. Their circulatory system is efficient at delivering oxygen to vital organs, and their metabolism slows down to reduce oxygen consumption. Additionally, dolphins have a high tolerance for carbon dioxide, which allows them to stay submerged for extended periods without experiencing discomfort.
In conclusion, dolphin anatomy is a fascinating subject that showcases the remarkable adaptations of these marine mammals. Their streamlined body shape, powerful fluke, sophisticated echolocation system, large eyes, and efficient circulatory system all contribute to their success in the ocean environment.
Transition to the next article section:
Conclusion
The exploration of dolphin anatomy reveals a symphony of adaptations that enable these marine mammals to thrive in their oceanic environment. From their streamlined bodies for efficient swimming to their powerful flukes for propulsion, every aspect of their anatomy showcases the remarkable evolutionary journey of dolphins.
The intricate echolocation system of dolphins grants them a unique ability to navigate and find prey in murky waters, while their large eyes provide a wide field of vision, both above and below the surface. Their small lungs and efficient circulatory system allow them to conserve oxygen during deep dives, showcasing their physiological marvels.
Understanding dolphin anatomy not only deepens our appreciation for these fascinating creatures but also highlights the importance of marine conservation. By safeguarding their habitats and reducing pollution, we can ensure the continued survival of these incredible animals and the delicate ecosystems they inhabit.


Detail Author:
- Name : Janet Larson
- Username : keeling.guadalupe
- Email : owatsica@jenkins.org
- Birthdate : 2001-06-28
- Address : 4296 Wiegand Orchard Apt. 748 Francescaport, AR 25704-2267
- Phone : 440.960.6567
- Company : Heidenreich, Price and Larson
- Job : Pressing Machine Operator
- Bio : Officiis qui non dolorem. Rerum rerum quaerat consequuntur laudantium vero facilis. Quisquam consequuntur molestiae enim quam eum facere.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/elwin423
- username : elwin423
- bio : Molestiae eum omnis animi ullam aut occaecati.
- followers : 1824
- following : 1915
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/elakin
- username : elakin
- bio : Hic eum ipsa quos architecto qui consequatur illo enim. Pariatur sed quas maxime ut.
- followers : 6071
- following : 80
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@elakin
- username : elakin
- bio : Et doloremque ipsam sed enim. Sed quo perferendis iusto.
- followers : 4274
- following : 1427